Micro_TP2
TP2 Rapport de Micro
JIN Zhuoyuan 22213816
Ex1
1.1
| Op1 | Op2 | Type d’opération | Résultat | N | Z | C | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x08000000 | 0x07000000 | + | 0x0F000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - | 0x01000000 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 0x40000000 | 0x40000000 | + | 0x80000000 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0x40000000 | 0x80000000 | - | 0xC0000000 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0x00F00000 | 0xFFFFFFFF | + | 0x00EFFFFF | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0x7F000000 | 0x0F000000 | + | 0x8E000000 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| - | 0x70000000 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 0x0F000000 | 0x7F000000 | + | 0x8E000000 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| - | 0x90000000 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | .data |
1.2
1 | .data |
resultat: 0x0F000000 01000004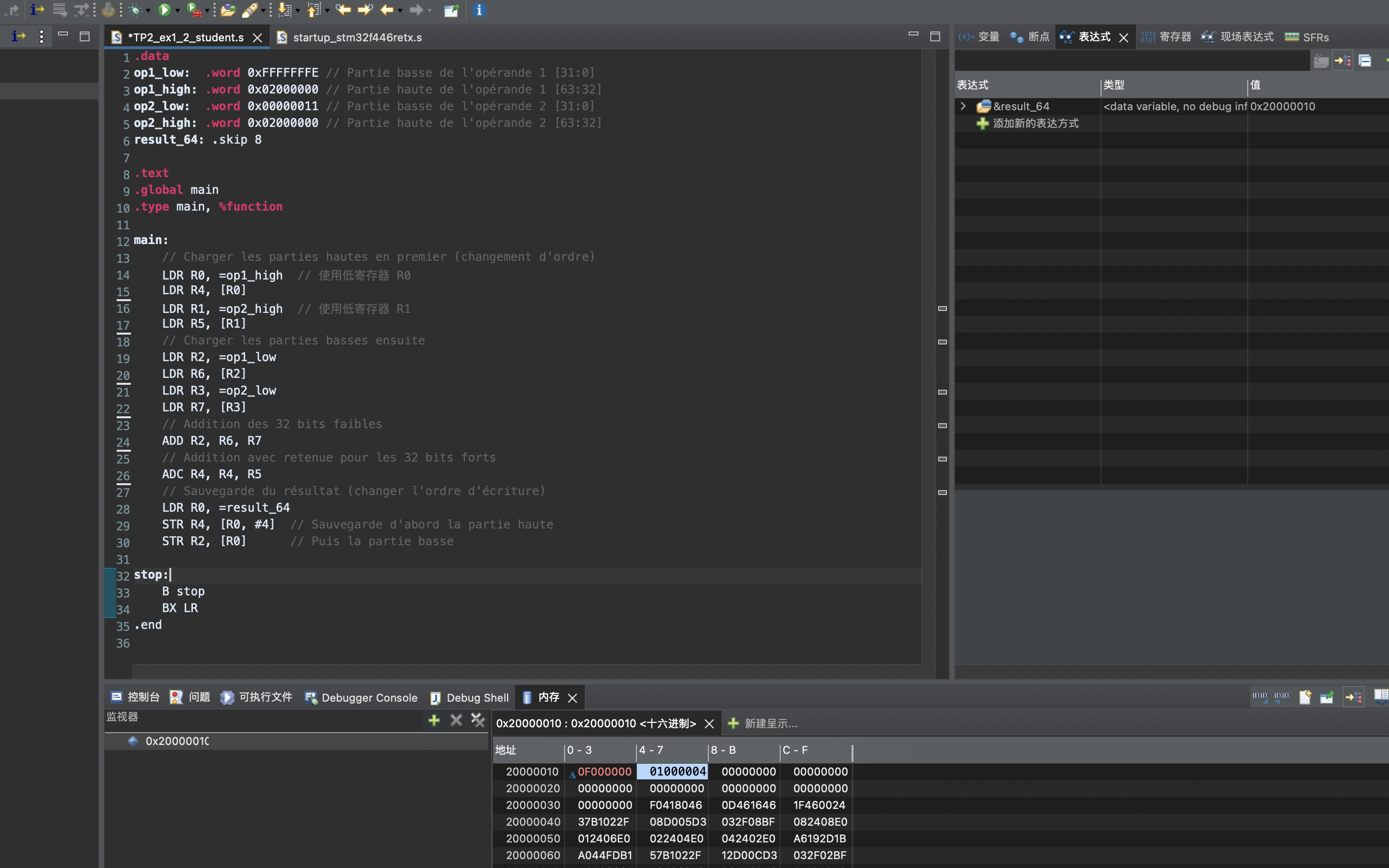
1.3
1 |
|
- AND est utilisé pour conserver certains bits et effacer les autres.
- ORR est utilisé pour définir certains bits.
- BIC est utilisé pour effacer des bits spécifiques.
- LSL (décalage logique à gauche) est utilisé pour accélérer la multiplication (×2ⁿ).
- ASR (décalage arithmétique à droite) est utilisé pour la division des nombres signés.
- LSR (décalage logique à droite) ne préserve pas le bit de signe.
- EOR (ou exclusif) est utilisé pour inverser certains bits.
- BIC (effacement de bits) est utilisé pour masquer certains bits.
Ex2 Suite de Fibonacci
La suite de Fibonacci est une suite d’entiers dont chaque terme est la somme des deux termes précédents. Les deux premiers termes permettent de démarrer le calcul et sont initialisés à 0 et 1 respectivement.
On note donc que :
F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2)
2.1
1 |
|
Resultat: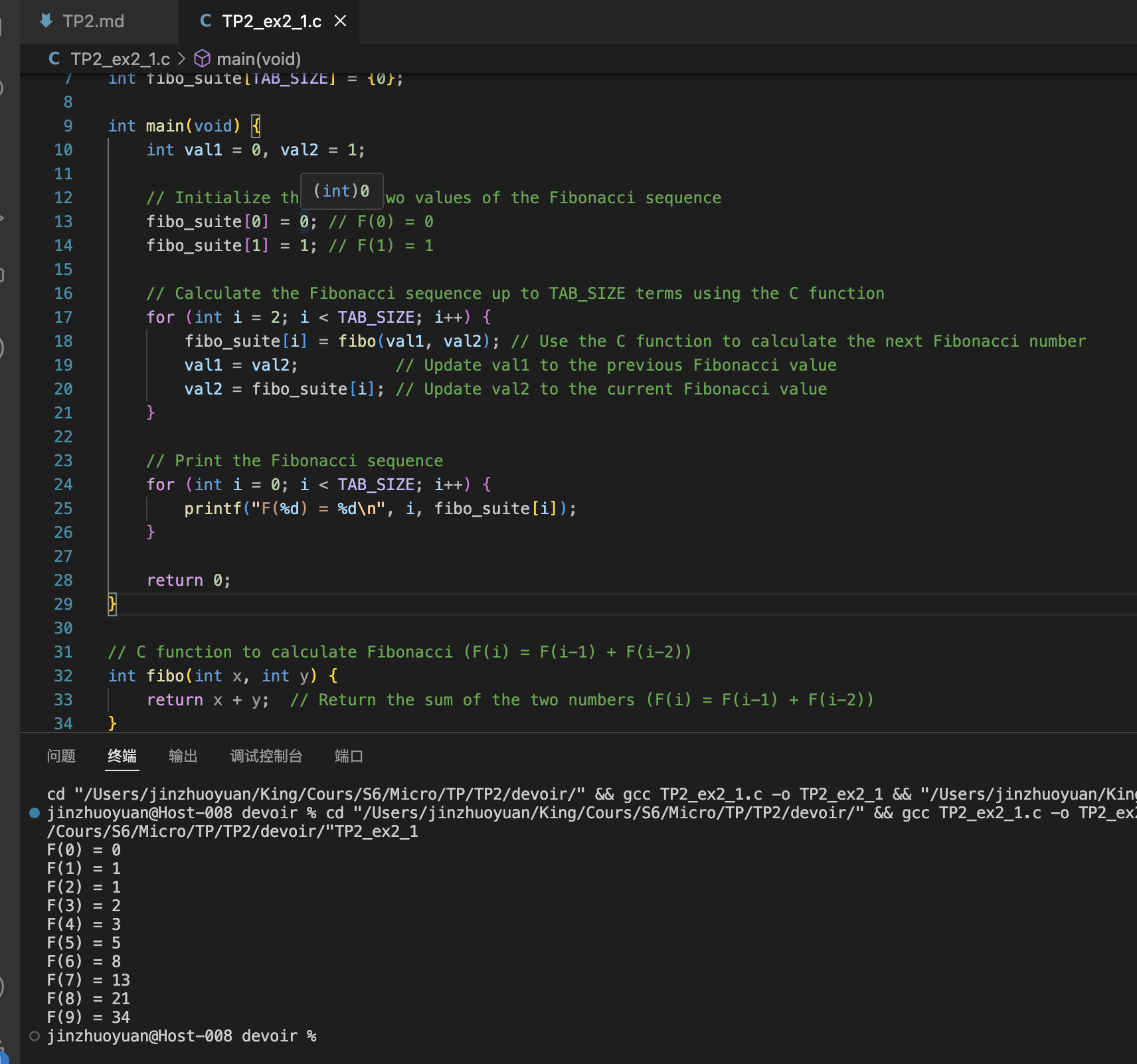
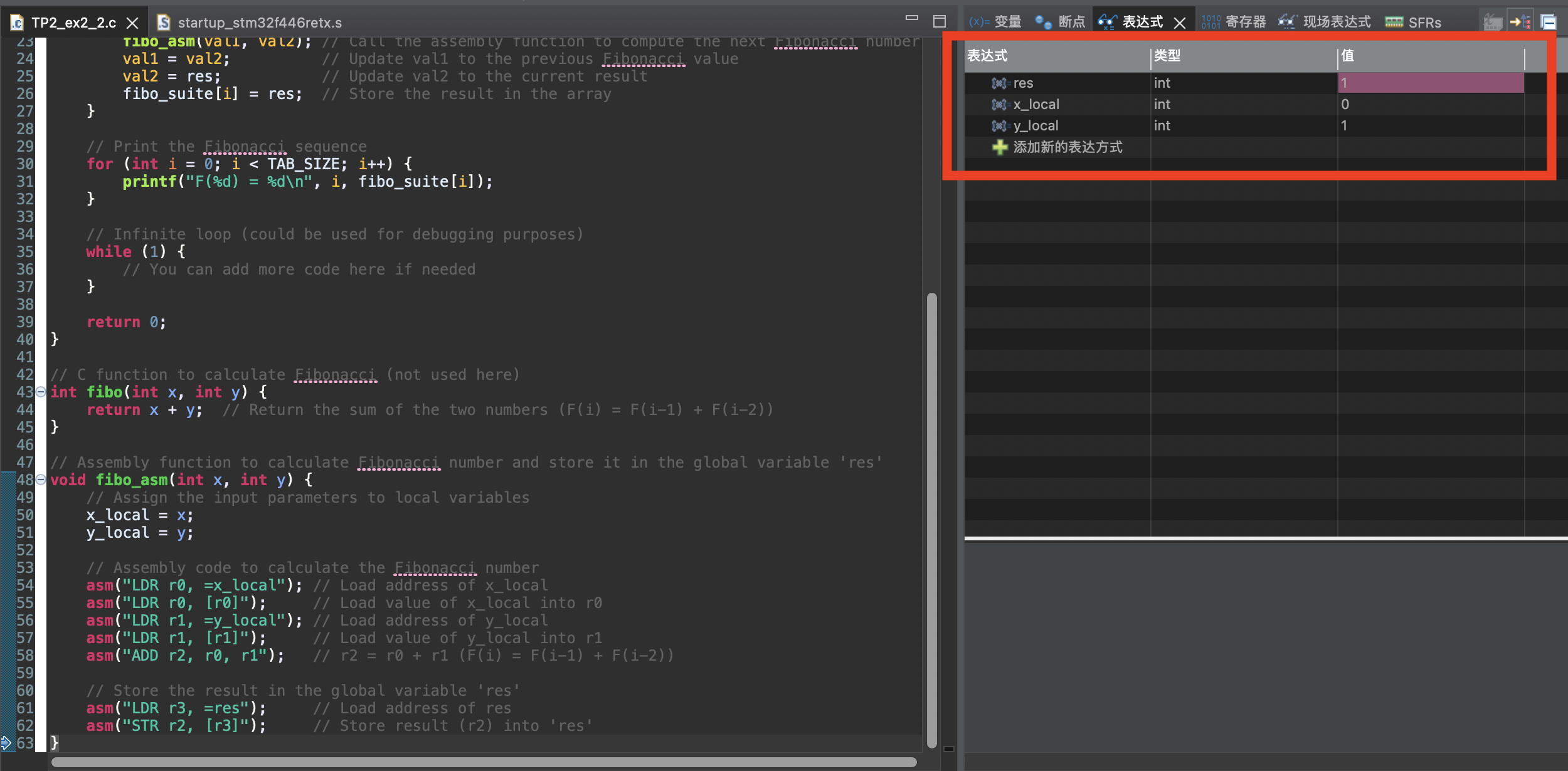
2.2
1 |
|
- x=0 y=1 res=1
- x=1 y=1 res=2
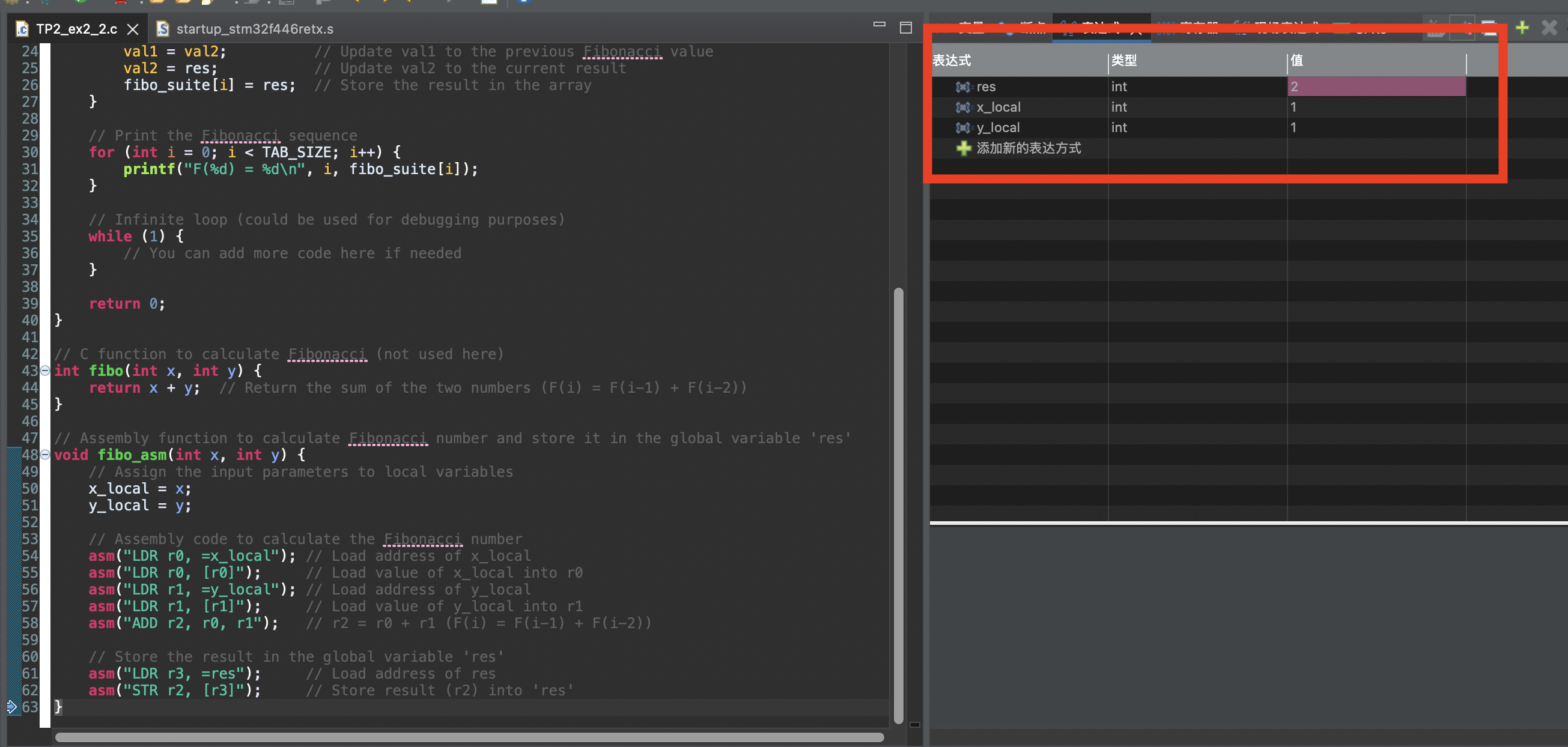
- x=1 y=2 res=3
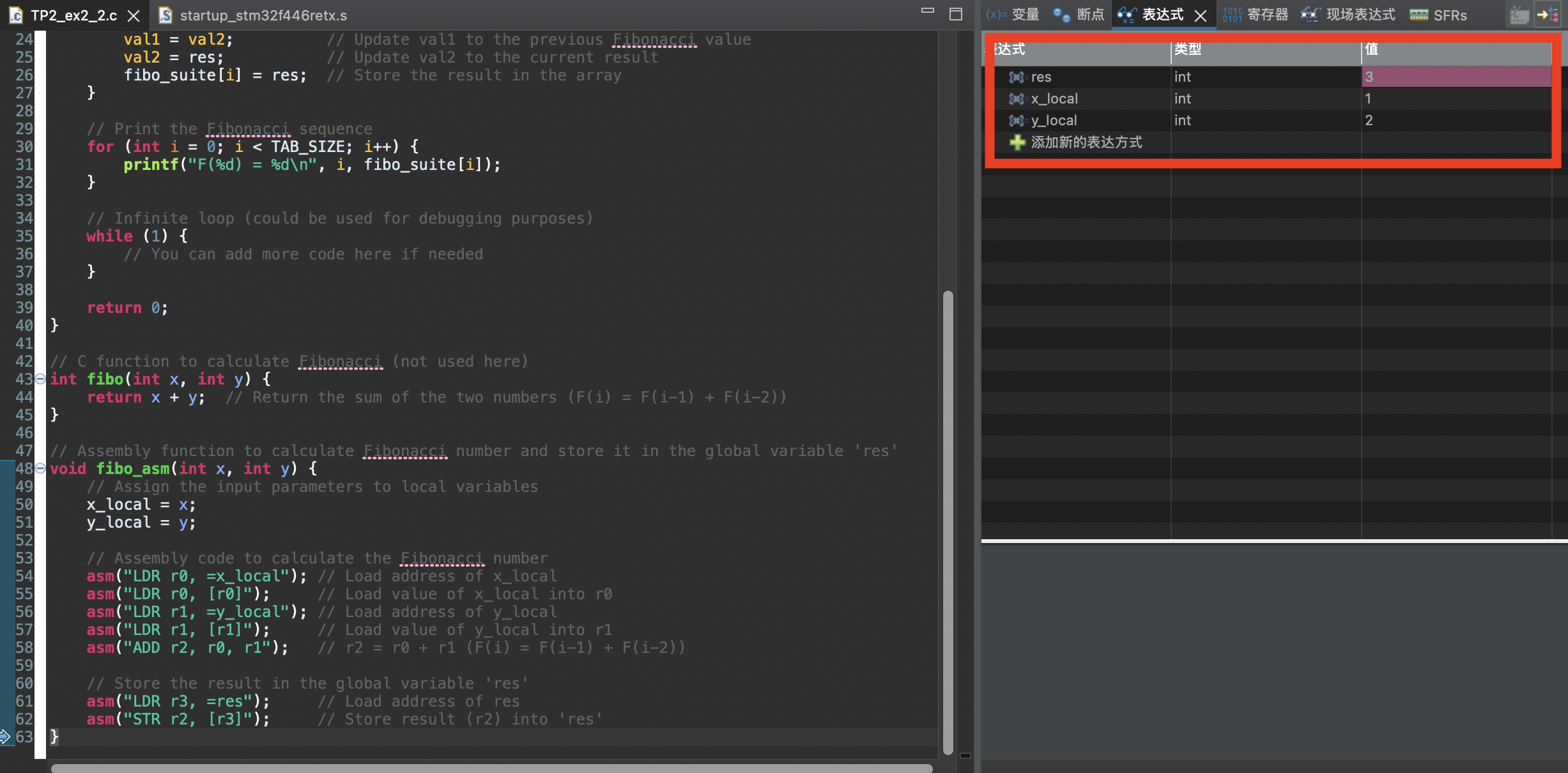
après c’est kif-kif
……
- x=13 y=21 res=34
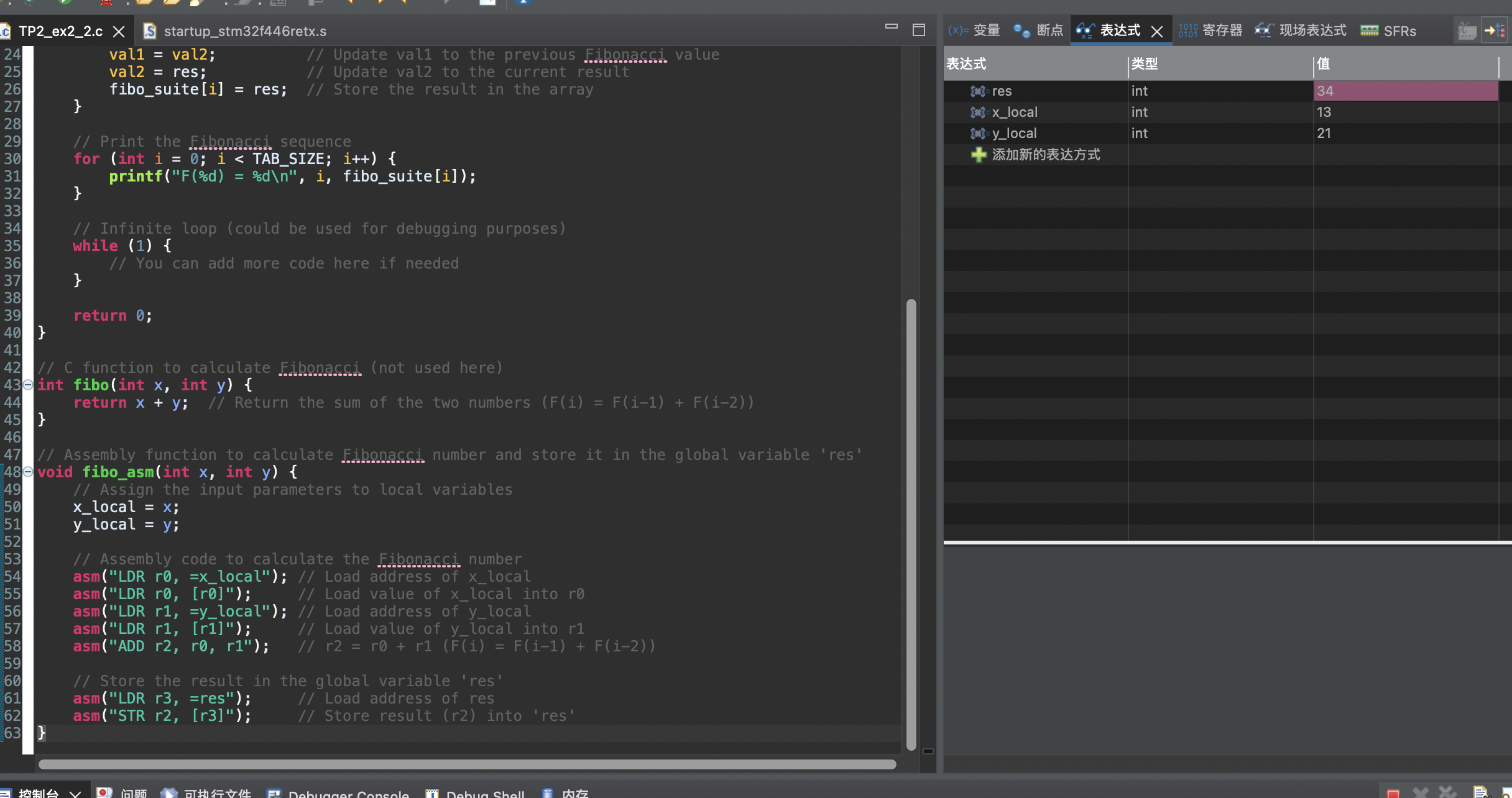
Ex3
C:
1 | int count_e(char* tab){ |
resultat: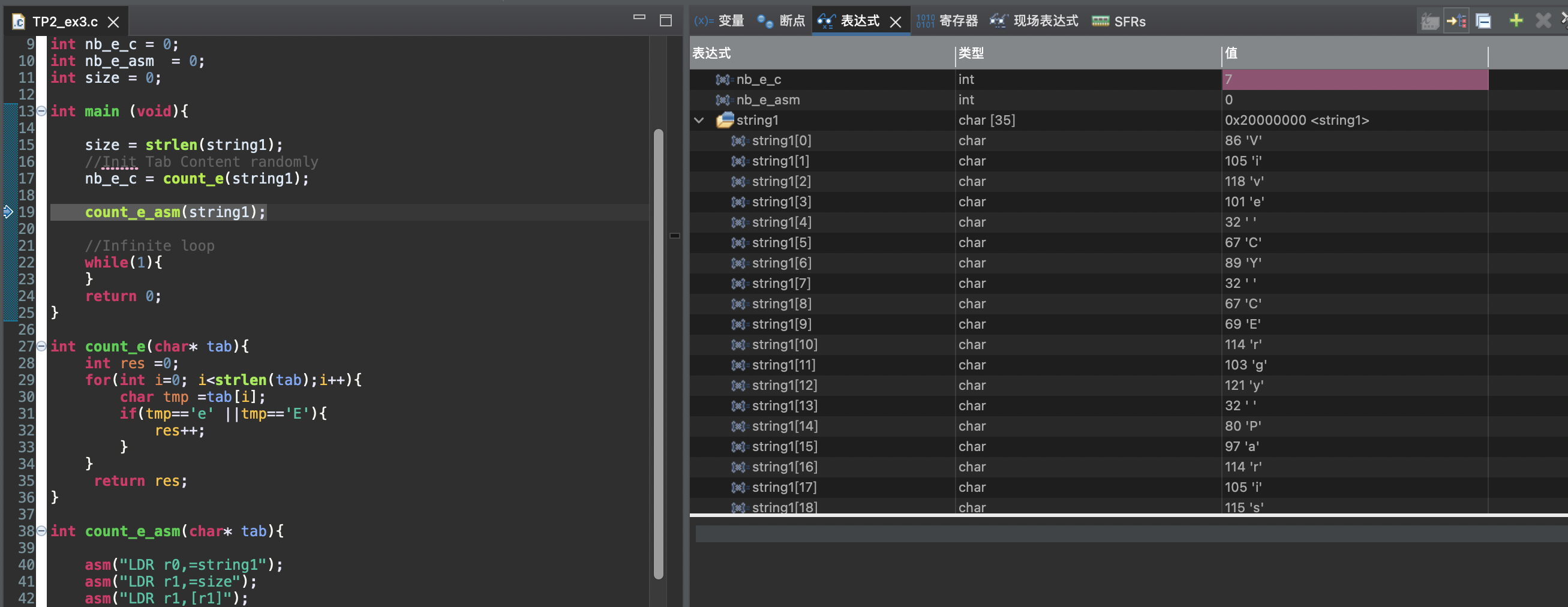
asm
1 | int count_e_asm(char* tab){ |
resultat: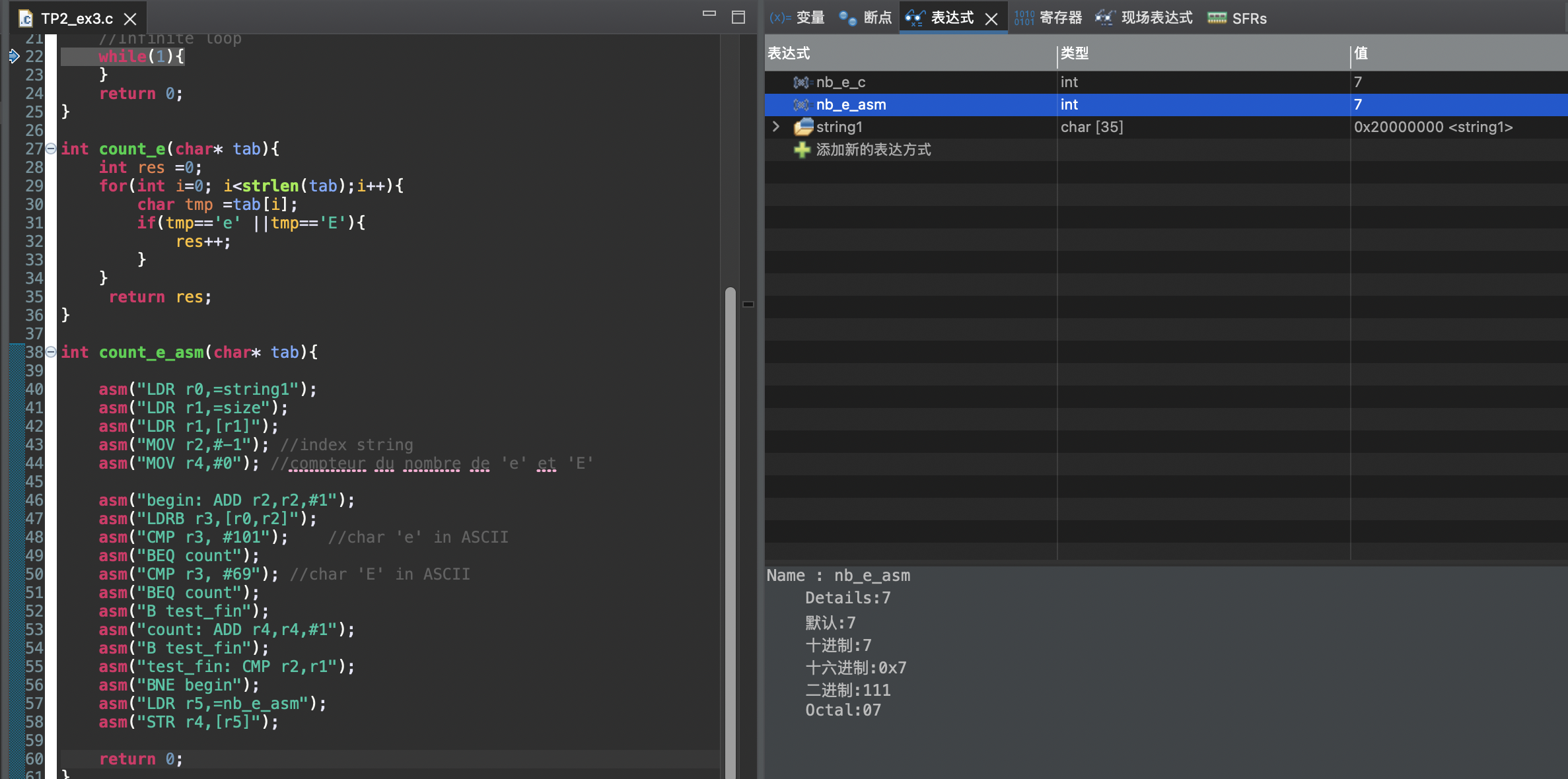
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 Elie Blog!
评论






